One of the most tragic parts of being human is being afflicted by diseases with high morbidity and mortality. Here is our list of top 10 deadliest diseases ever known to man.
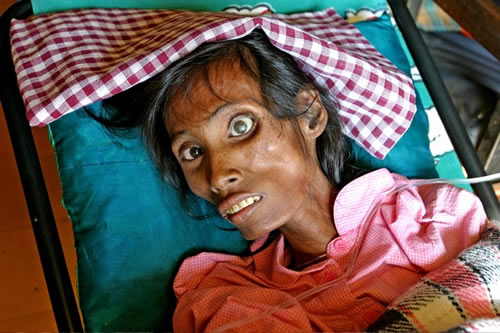 1. AIDS; 25 million from 1981 to present
1. AIDS; 25 million from 1981 to present
AIDS is a mix of infections and complications as a result of progressive damage to the body�s immune system caused by HIV. AIDS is now considered a pandemic.
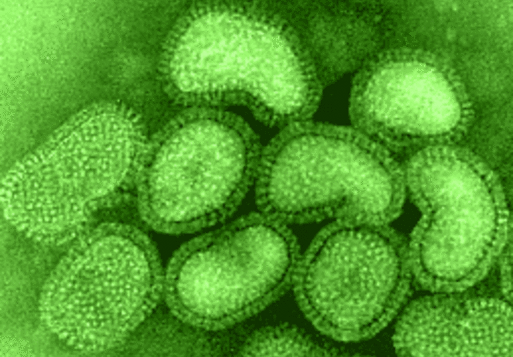 2. Influenza; 36,000 deaths annually
2. Influenza; 36,000 deaths annually
Influenza, which is more commonly known as flu, is a highly infectious disease that is caused by influenza virus. Transmission of the disease is by airborne and through physical contact.
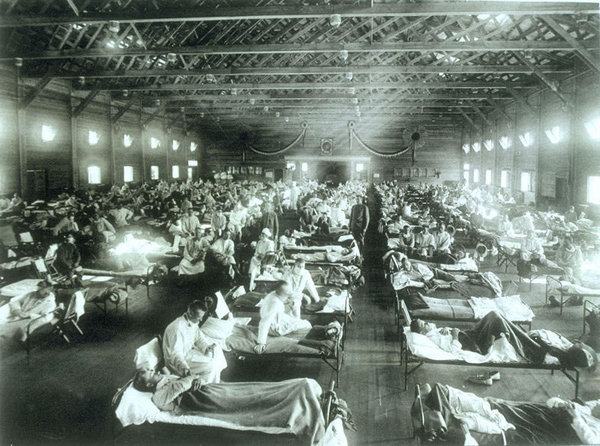 3. Spanish Flu, 1918-19; 100 million deaths
3. Spanish Flu, 1918-19; 100 million deaths
The flu pandemic that happened in 1918 is termed as a category 5 flu pandemic which was caused by the flu virus strain A with subtype H1N1.
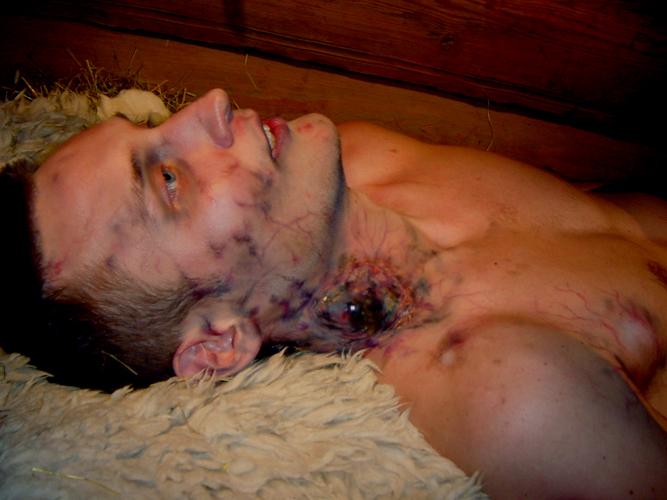 4. Bubonic Plague; 250 million deaths
4. Bubonic Plague; 250 million deaths
This disease outbreak was mainly caused by fleas and rodents infected with Xenopsylla cheopsis. Humans were infected after being bitten by an affected rodent.
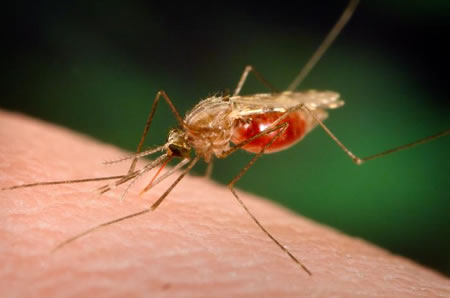 5. Malaria; 2.7 million deaths annually
5. Malaria; 2.7 million deaths annually
Malaria is an infectious disease which is vector-borne. The causative agent is the protozoan parasites. It is a common disease in the sub-tropics and tropical regions.
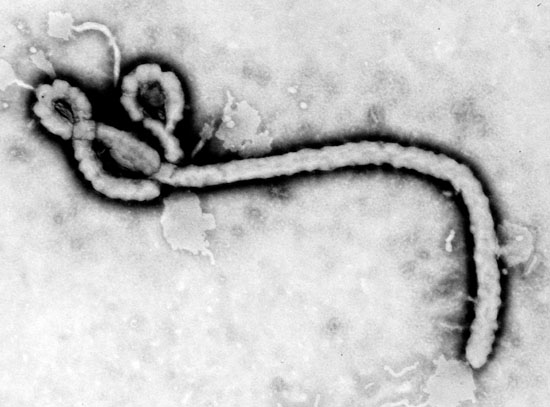 6. Ebola; 160,000 deaths from 2000 to present
6. Ebola; 160,000 deaths from 2000 to present
The Ebola virus was first isolated in1976 from the dual outbreaks that occurred in Zaire and Sudan. It is a zoonotic disease as it affects lowland apes as well as humans.
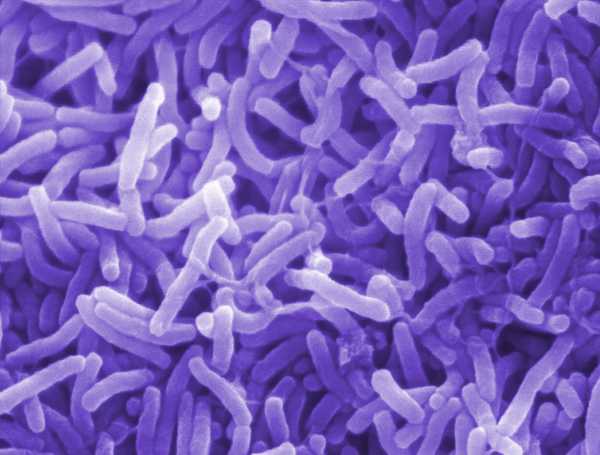 7. Cholera; 12,000 deaths from 1991 to present
7. Cholera; 12,000 deaths from 1991 to present
The epidemic or Asiatic cholera is a very serious type of diarrheal ailment caused by Vibrio cholera. The mode of transmission is by ingesting contaminated food and water.
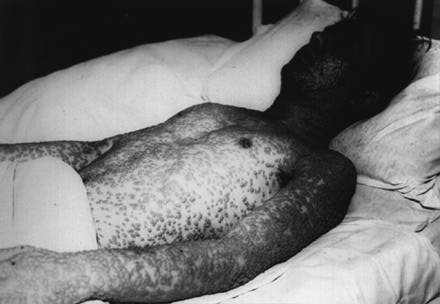 8. Smallpox; Population drop from 12 million to 235,000
8. Smallpox; Population drop from 12 million to 235,000
Smallpox is a highly contagious viral disease that has two variants. The V major has a 35% mortality rate while the less severe V minor has a 1% mortality rate.
 9. Polio, 10,000 deaths from 1916 to present
9. Polio, 10,000 deaths from 1916 to present
Polio or infantile paralysis is a viral disease that is transmitted through the fecal-oral course.
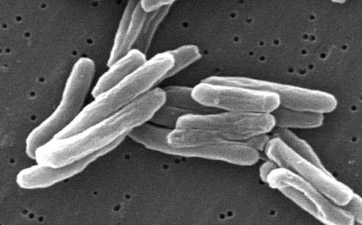 10. Tuberculosis; 75 million deaths
10. Tuberculosis; 75 million deaths
Tuberculosis is life-threatening if not treated promptly and for the elderly, infants, and people with a compromised immune system. The disease has resulted in around 100 million fatalities in the 20th century.
 1. AIDS; 25 million from 1981 to present
1. AIDS; 25 million from 1981 to presentAIDS is a mix of infections and complications as a result of progressive damage to the body�s immune system caused by HIV. AIDS is now considered a pandemic.
 2. Influenza; 36,000 deaths annually
2. Influenza; 36,000 deaths annuallyInfluenza, which is more commonly known as flu, is a highly infectious disease that is caused by influenza virus. Transmission of the disease is by airborne and through physical contact.
 3. Spanish Flu, 1918-19; 100 million deaths
3. Spanish Flu, 1918-19; 100 million deathsThe flu pandemic that happened in 1918 is termed as a category 5 flu pandemic which was caused by the flu virus strain A with subtype H1N1.
 4. Bubonic Plague; 250 million deaths
4. Bubonic Plague; 250 million deathsThis disease outbreak was mainly caused by fleas and rodents infected with Xenopsylla cheopsis. Humans were infected after being bitten by an affected rodent.
 5. Malaria; 2.7 million deaths annually
5. Malaria; 2.7 million deaths annuallyMalaria is an infectious disease which is vector-borne. The causative agent is the protozoan parasites. It is a common disease in the sub-tropics and tropical regions.
 6. Ebola; 160,000 deaths from 2000 to present
6. Ebola; 160,000 deaths from 2000 to presentThe Ebola virus was first isolated in1976 from the dual outbreaks that occurred in Zaire and Sudan. It is a zoonotic disease as it affects lowland apes as well as humans.
 7. Cholera; 12,000 deaths from 1991 to present
7. Cholera; 12,000 deaths from 1991 to presentThe epidemic or Asiatic cholera is a very serious type of diarrheal ailment caused by Vibrio cholera. The mode of transmission is by ingesting contaminated food and water.
 8. Smallpox; Population drop from 12 million to 235,000
8. Smallpox; Population drop from 12 million to 235,000Smallpox is a highly contagious viral disease that has two variants. The V major has a 35% mortality rate while the less severe V minor has a 1% mortality rate.
 9. Polio, 10,000 deaths from 1916 to present
9. Polio, 10,000 deaths from 1916 to presentPolio or infantile paralysis is a viral disease that is transmitted through the fecal-oral course.
 10. Tuberculosis; 75 million deaths
10. Tuberculosis; 75 million deathsTuberculosis is life-threatening if not treated promptly and for the elderly, infants, and people with a compromised immune system. The disease has resulted in around 100 million fatalities in the 20th century.
















No comments:
Post a Comment